In the quest for sustainable energy sources, biomass has emerged as a promising frontier, revolutionizing the renewable energy landscape. Biomass refers to organic materials derived from plants and animals, such as wood, agricultural residues, and even municipal waste. These materials, when converted through various processes, can yield biofuels and biogas, offering a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Let’s delve into how biomass is driving this Renewable Energy revolution.
The Promise of Biomass
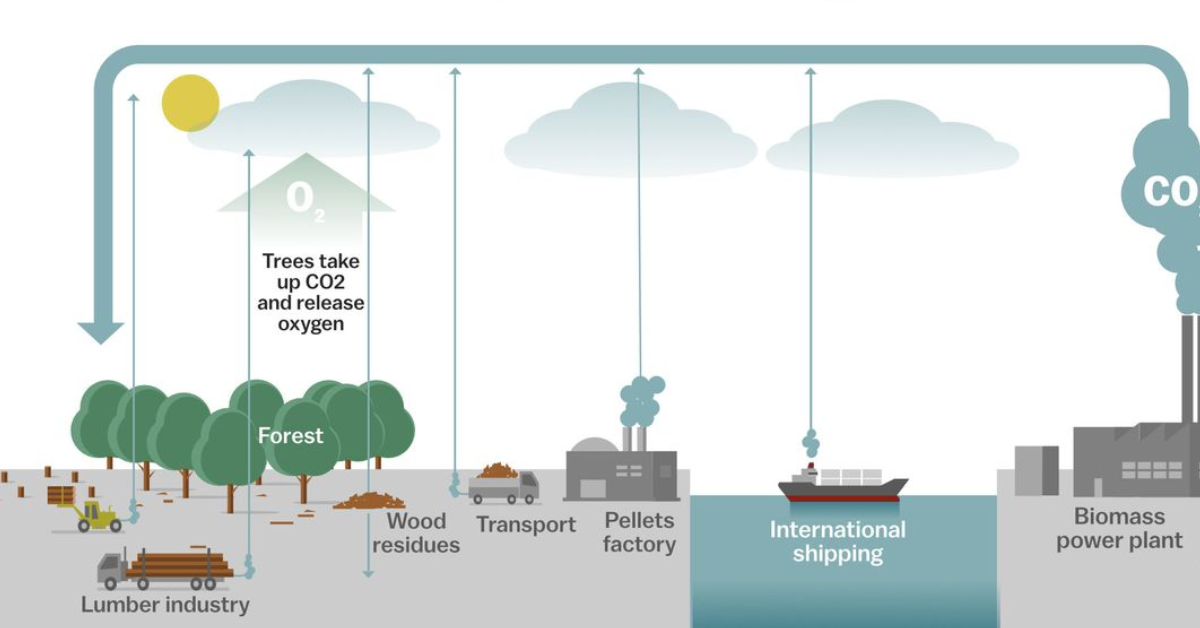
Biomass holds immense promise due to its renewable nature and abundance. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, biomass is part of the natural carbon cycle. When plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This carbon is then released back into the atmosphere when biomass is burned for energy, creating a closed carbon loop that doesn’t contribute to a net increase in greenhouse gases.
Bioenergy: Powering the Future
One of the key ways biomass is revolutionizing renewable energy is through bioenergy production. Bioenergy encompasses various processes, including:
Biofuels: Biomass can be converted into liquid biofuels such as biodiesel and bioethanol. These biofuels can be used to power vehicles, replacing or supplementing traditional fossil fuels. With advancements in biofuel production technology, such as cellulosic ethanol production from agricultural waste, the efficiency and sustainability of biofuels continue to improve.
Biogas: Through anaerobic digestion, organic waste materials like agricultural residues, food waste, and sewage sludge can be converted into biogas. Biogas is primarily composed of methane and can be used for heat and electricity generation, making it a valuable source of renewable energy.
Environmental Benefits
The shift towards biomass-based renewable energy offers significant environmental benefits:
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: By utilizing biomass for energy production, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower emissions of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane.
Waste Management: Biomass energy systems can help manage organic waste, reducing landfill usage and methane emissions from decomposing waste.
Sustainable Land Use: Biomass can be sourced from sustainable forestry practices, agricultural residues, and other renewable sources, promoting responsible land management.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in biomass conversion technologies are driving the efficiency and scalability of biomass-based energy systems. These include:
Gasification: Converting biomass into syngas through gasification allows for the production of heat, electricity, and biofuels.
Pyrolysis: Thermal decomposition of biomass in the absence of oxygen can yield bio char, bio-oil, and syngas, each with specific energy applications.
Integrated Bio refineries: These facilities integrate multiple biomass conversion processes to maximize energy output and resource utilization.
Economic Opportunities
The biomass sector presents economic opportunities across various fronts:
Job Creation: From biomass cultivation and collection to processing and energy generation, the biomass industry supports job creation in rural and urban areas.
Local Development: Biomass energy projects can spur local economic development, especially in regions with abundant biomass resources.
Energy Security: Diversifying energy sources with biomass reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security at the national and regional levels.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While biomass offers significant advantages, challenges such as resource availability, land use competition, and technological complexity remain. Addressing these challenges requires continued research, policy support, and investment in infrastructure.
Looking ahead, the integration of biomass with other renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, along with advancements in energy storage technologies, will further enhance the reliability and sustainability of biomass-based energy systems.
In conclusion, biomass is a cornerstone of the renewable energy revolution, offering a versatile, sustainable, and economically viable alternative to fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of biomass, we can accelerate the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.